Wi-LiFi: Integrated Optical Wi-Fi for Enhanced Mobile Robotic Communications
Overview


The field of robotics and automation heavily relies on effective communication among multiple robots to accomplish collaborative tasks. However, communication interference often poses a challenge in multi-robot systems, especially when using traditional wireless technologies such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. To overcome these limitations, Optical Wireless Communication (OWC) has emerged as a promising solution, offering virtually unlimited spectrum resources and high spectral efficiency. While existing OWC products focus on fixed point-to-point communication, this paper presents a novel design and implementation of an omnidirectional optical transceiver for inter-robot communication in mobile scenarios.
Main Contribution
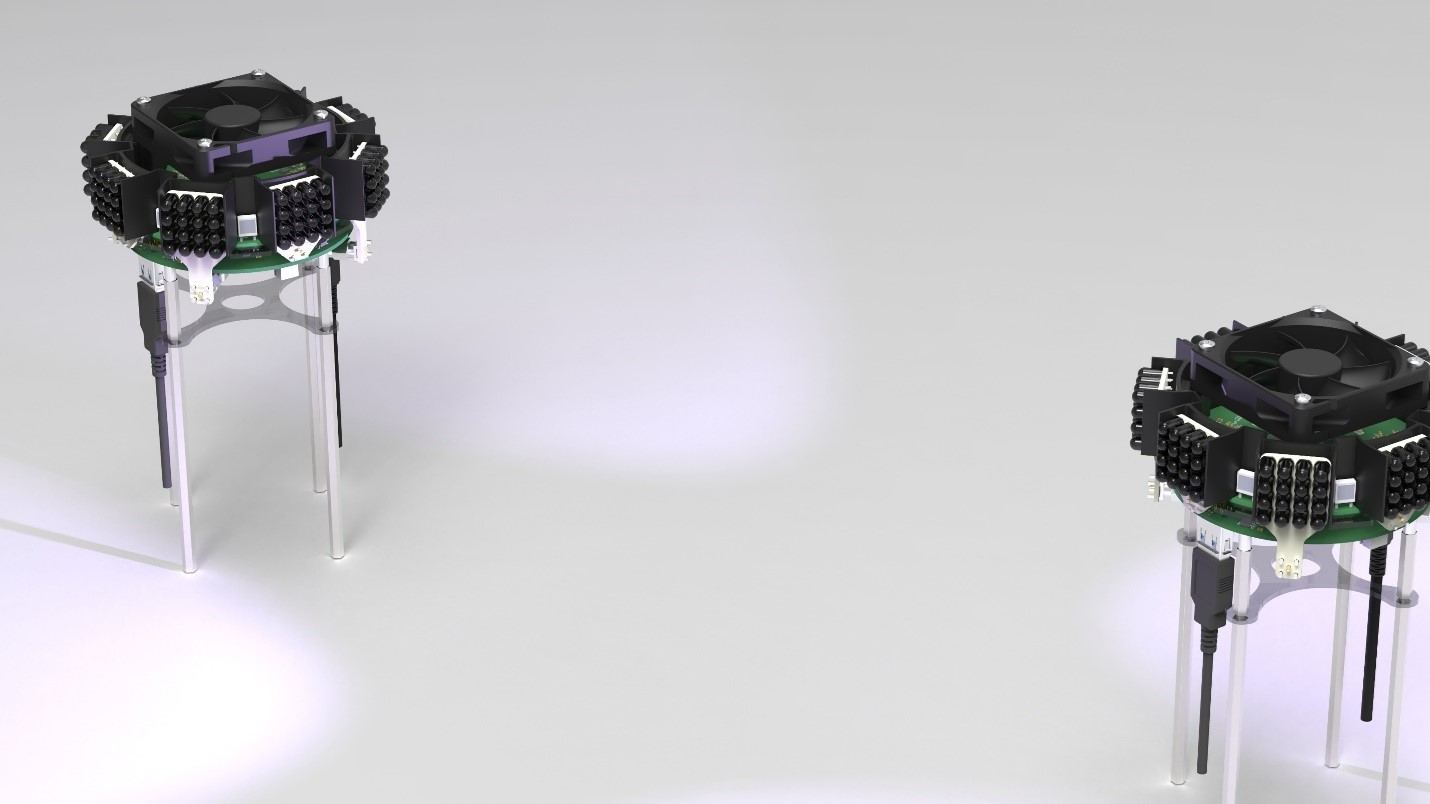
The main contribution of this work is the development of an omnidirectional optical transceiver that aligns with the IEEE 802.11bb standard and is compatible with commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) Wi-Fi cards. Unlike previous designs, our transceiver operates as a plug-and-play optical antenna, replacing the RF antenna without requiring modifications to the Wi-Fi card. The transceiver utilizes a multi-emitter, multi-detector approach to achieve omnidirectional coverage, ensuring reliable and consistent optical connections as robots move. Additionally, a hardware-based diversity combining method, implemented using a low-cost microcontroller unit (MCU), enables real-time and effective signal combination from multiple photodiodes (PDs) at the receiver. This method eliminates the need for complex sampling and demodulation processes, reducing hardware costs while maintaining high data rates.
By introducing this omnidirectional optical transceiver, our system enables high-speed inter-robot communication using light at data rates comparable to Wi-Fi. Experimental results demonstrate stable and high-speed optical links exceeding 30 Mbps over distances of more than 3 meters. Moreover, the system maintains reliable optical connections even in dynamic, mobile scenarios. The compatibility with COTS Wi-Fi cards and the ability to handle mobility make our transceiver a practical and cost-effective solution for optical inter-robot communication, addressing a significant gap in the existing literature.